Overcoming Challenges in Roll-to-Roll Manufacturing: A Comprehensive Review of System Modeling and Control
Introduction
Roll-to-roll (R2R) manufacturing has long been recognized as an efficient and cost-effective production method for industries such as paper, textiles, and flexible packaging. In recent years, its applications have expanded to high-tech manufacturing, including flexible electronics, printed solar cells, battery production, and 2D materials. These new applications demand higher precision, better control systems, and more advanced modeling techniques to maintain product quality and production efficiency. Based on the review article "A Review of Advanced Roll-to-Roll Manufacturing: System Modeling and Control", by Martin et al., this blog post provides a detailed analysis of modeling and control approaches in R2R systems, examining current challenges, key advancements, and future directions for improving precision and efficiency.
Traditional R2R manufacturing was primarily designed for bulk material processing, but modern applications require much tighter tolerances and real-time process adjustments. Achieving high precision in web tension, positioning, and environmental stability is essential for enabling the next generation of advanced materials. This requires a thorough understanding of how materials behave under continuous motion and how control systems can be optimized to reduce error propagation, slippage, and defects.
This blog post explores the core elements of R2R system modeling and control, structured around two key areas:
System modeling, which helps predict material behavior and process interactions.
Advanced control strategies, which ensure stable, high-quality production through real-time adjustments and automation.
Key Highlights
R2R manufacturing faces challenges in precision control, especially for flexible electronics and battery production.
Traditional physics-based modeling is widely used but lacks flexibility; hybrid models combining physics and real-time data offer a promising solution.
Advanced control methods, such as H∞-optimal control, adaptive controllers, and iterative learning control (ILC), enhance system performance.
Decentralized control is common in R2R systems, but more centralized methods may improve accuracy.
Addressing inter-subsystem error transfer is critical for maintaining production quality.
Low-tension web control is crucial for thin-film applications to prevent deformation.
Future research should focus on hybrid modeling, viscoelasticity, and improving MIMO control strategies
Discover everything you need to know about slot-die coating in our comprehensive guide.
1. The Evolution and Challenges of Roll-to-Roll Manufacturing
The fundamental appeal of R2R manufacturing lies in its continuous processing capability, which significantly reduces production time and cost compared to traditional batch manufacturing. However, as it moves into applications like printed electronics and thin-film solar cells, the requirements for precision are far greater.
Key challenges include:
Web tension control – Ensuring that flexible substrates remain stable without excessive stretching or slack.
Positioning accuracy – Preventing lateral drift or misalignment, which can cause defects.
Periodic disturbances – Addressing errors introduced by roller imperfections, mechanical vibrations, or environmental changes.
Material variability – Managing materials with varying mechanical properties, such as viscoelasticity in thin films.
As these challenges become more complex, modeling and control strategies must evolve to maintain high throughput while minimizing material waste and defects.
2. Roll-to-Roll System Modeling: Understanding Process Dynamics
Precise system modeling is essential for predicting and controlling the behavior of R2R manufacturing processes. The review categorizes modeling efforts into several critical areas, each addressing specific process dynamics that affect production quality.
2.1 Longitudinal Web Dynamics
Longitudinal web dynamics refer to how the substrate moves through the R2R system. Controlling web tension and velocity in this direction is essential for maintaining product consistency. If tension fluctuates too much, it can lead to material deformation, tearing, or misalignment in downstream processes.
Researchers have developed multi-span tension models that account for the complex interactions between different sections of the web. These models use strain transport equations to predict how variations in tension affect subsequent stages of processing. Advanced real-time feedback mechanisms have also been introduced to adjust web velocity dynamically, ensuring that fluctuations do not propagate through the system.
2.2 Lateral Web Dynamics
While longitudinal dynamics focus on web movement along the process direction, lateral web dynamics deal with side-to-side motion. Any uncontrolled lateral movement can cause misalignment, leading to defects in printed patterns, coatings, or laminated layers.
To address this, researchers have applied beam-based models that describe how flexible materials behave under different force conditions. These models are particularly useful in predicting lateral displacement caused by roller misalignment or uneven tension distribution. Finite element modeling (FEM) has also been used to simulate lateral motion, allowing for more precise control strategies to be developed.
2.3 Web Slippage
Web slippage occurs when the material moves inconsistently relative to the rollers, typically due to low tension or sudden speed variations. This can lead to inconsistencies in coating thickness, print alignment, or material layering. To prevent slippage, friction-based models have been developed to predict when it is likely to occur. By understanding the interplay between web tension and roller friction, adaptive control strategies can be implemented to adjust torque and speed dynamically, ensuring smooth and consistent web transport.
2.4 Viscoelasticity
Many modern materials used in R2R processing, such as polymer films and thin coatings, exhibit viscoelastic behavior. This means their mechanical properties change over time, which can significantly affect tension control and print quality. If not accounted for, viscoelastic effects can lead to inconsistent adhesion, uneven stretching, and long-term instability in flexible electronic devices. Advanced modeling techniques now incorporate time-dependent material behavior, allowing for better prediction and compensation of these effects in real-time production environments.
2.5 Roller Eccentricity and Varying Web Span Length
In real-world production settings, rollers are not always perfectly shaped or aligned. Eccentric rollers can introduce periodic disturbances that cause fluctuations in tension and speed. To mitigate these effects, eccentricity detection algorithms have been developed to identify irregularities in roller motion. These algorithms work in conjunction with adaptive control systems that dynamically adjust motor speed and tension settings to compensate for mechanical imperfections.
Probably the world’s most compact R2R slot-die coater, featuring a syringe pump, a 65 mm slot-die head, and an infrared oven for precise lab coating.
2.6 Peeling Dynamics
For processes such as dry-transfer printing, where delicate films must be peeled and applied to a target substrate, precise control of peeling forces is crucial. If peeling is not properly controlled, adhesion can become inconsistent, leading to defects. The review highlights stick-slip modeling, which helps predict how peeling will behave under different process conditions. This allows for optimized peeling front energy management, improving adhesion consistency.
2.7 Thermal Effects
Many R2R processes involve drying, curing, or heating steps, which can significantly alter web tension and material properties. If not managed properly, thermal expansion and contraction can introduce defects in the final product. To address this, temperature-dependent strain models have been developed to predict how materials will react to heat exposure. These models are used to implement nonlinear control strategies, which adjust process parameters in real time to maintain stability.
2.8 Data-Driven Modeling
Recent advancements in machine learning and AI-driven system identification have opened new possibilities for R2R control. Instead of relying solely on physics-based models, real-time sensor data is now being used to train adaptive models that can predict system behavior more accurately. Hybrid approaches that combine physics-based equations with AI-driven learning are proving to be particularly effective, allowing for real-time optimization and improved process stability.
The Slot-die Coater is a state-of-the-art, compact sheet coater for precise, consistent slot-die coatings, featuring a vacuum chuck, integrated drying, and optimized ink delivery.
3. Advanced Control Strategies for R2R Systems
While traditional R2R systems have relied on PID controllers, modern applications require more sophisticated control techniques to manage increasing complexity.
Key Control Strategies Discussed in the Review:
Periodic Disturbance Control using H∞-optimal control and Iterative Learning Control (ILC) to counteract mechanical vibrations.
Decentralized vs. Centralized Control approaches, including overlapping decomposition methods for modular control.
Inter-Subsystem Error Transfer Prevention, minimizing error propagation between different stages of production.
Low-Tension Web Handling, crucial for flexible electronics and ultra-thin coatings.
Adaptive and Fault-Tolerant Control, incorporating self-learning algorithms to compensate for material variability and external disturbances.
4. Conclusion
The review by Martin et al. highlights the rapid advancements in R2R manufacturing, emphasizing the need for better modeling, smarter control systems, and real-time adaptability. As industries move toward high-precision, AI-driven production, these technologies will play a crucial role in shaping the future of flexible electronics, energy storage, and advanced materials manufacturing.
Authors
Christopher Martin
Qishen Zhao
Anjali Patel
Enrique Velasquez
Dongmei Chen
Wei Li
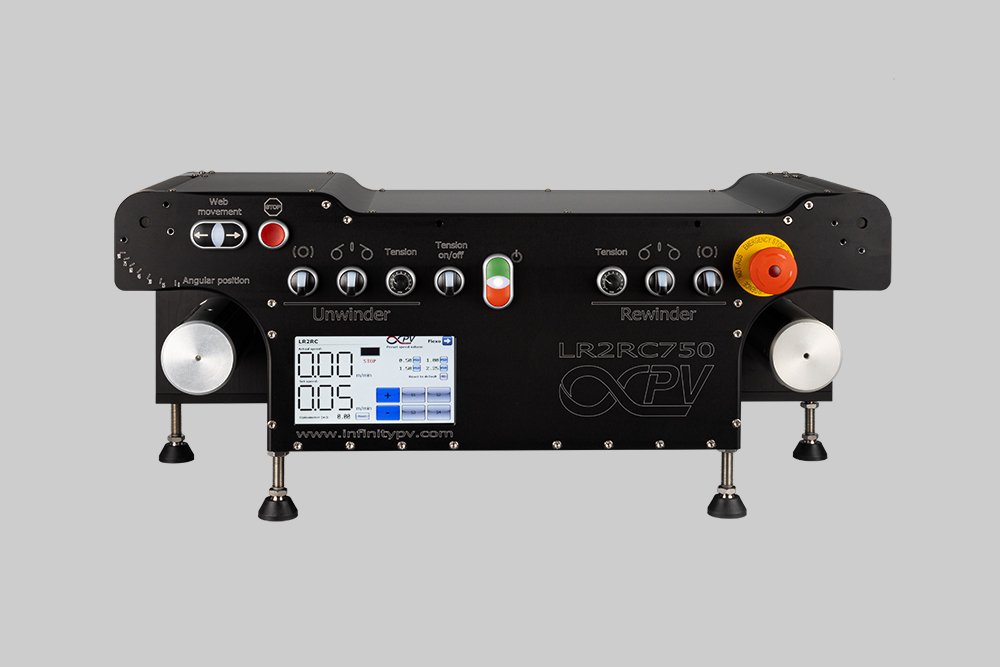
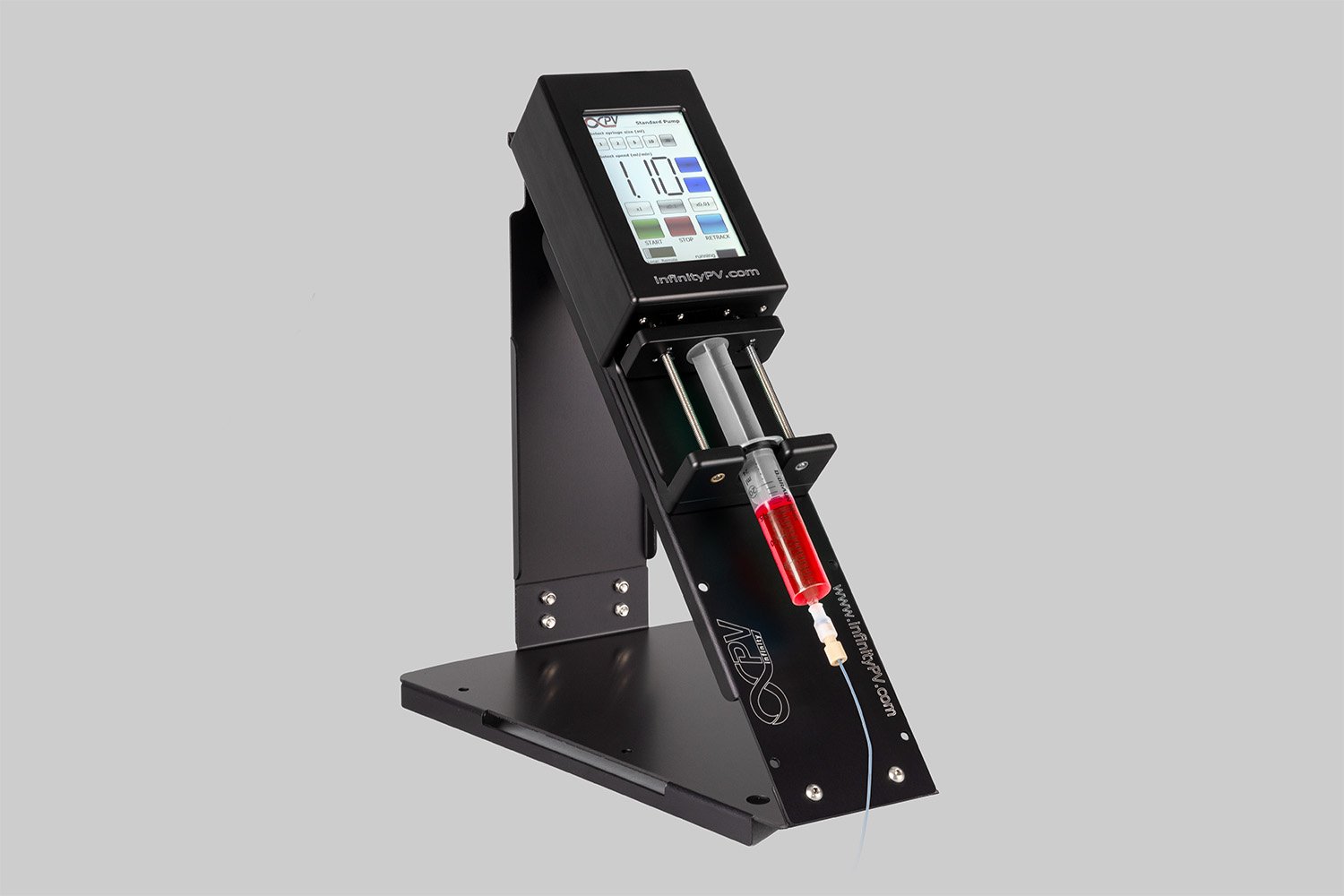
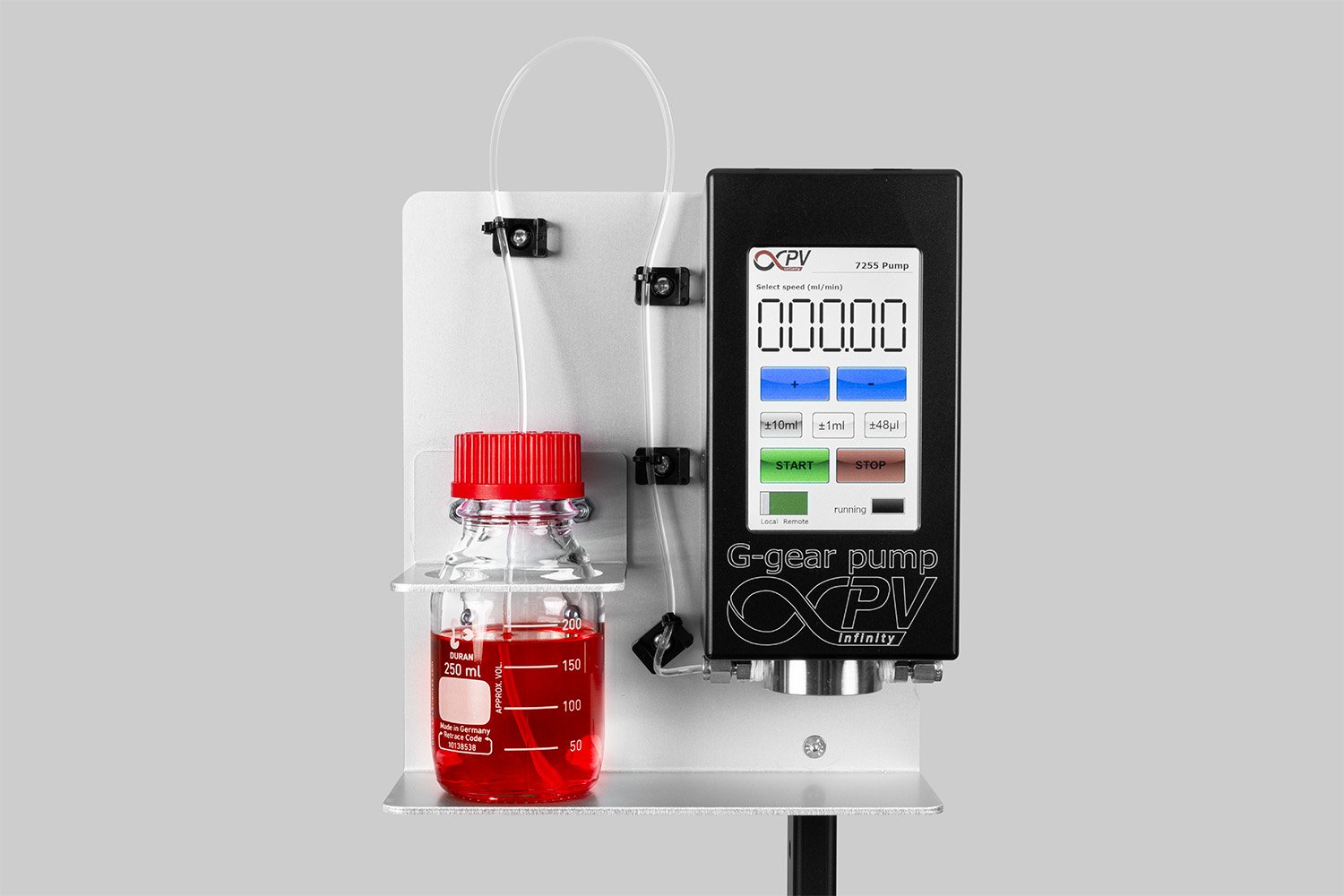
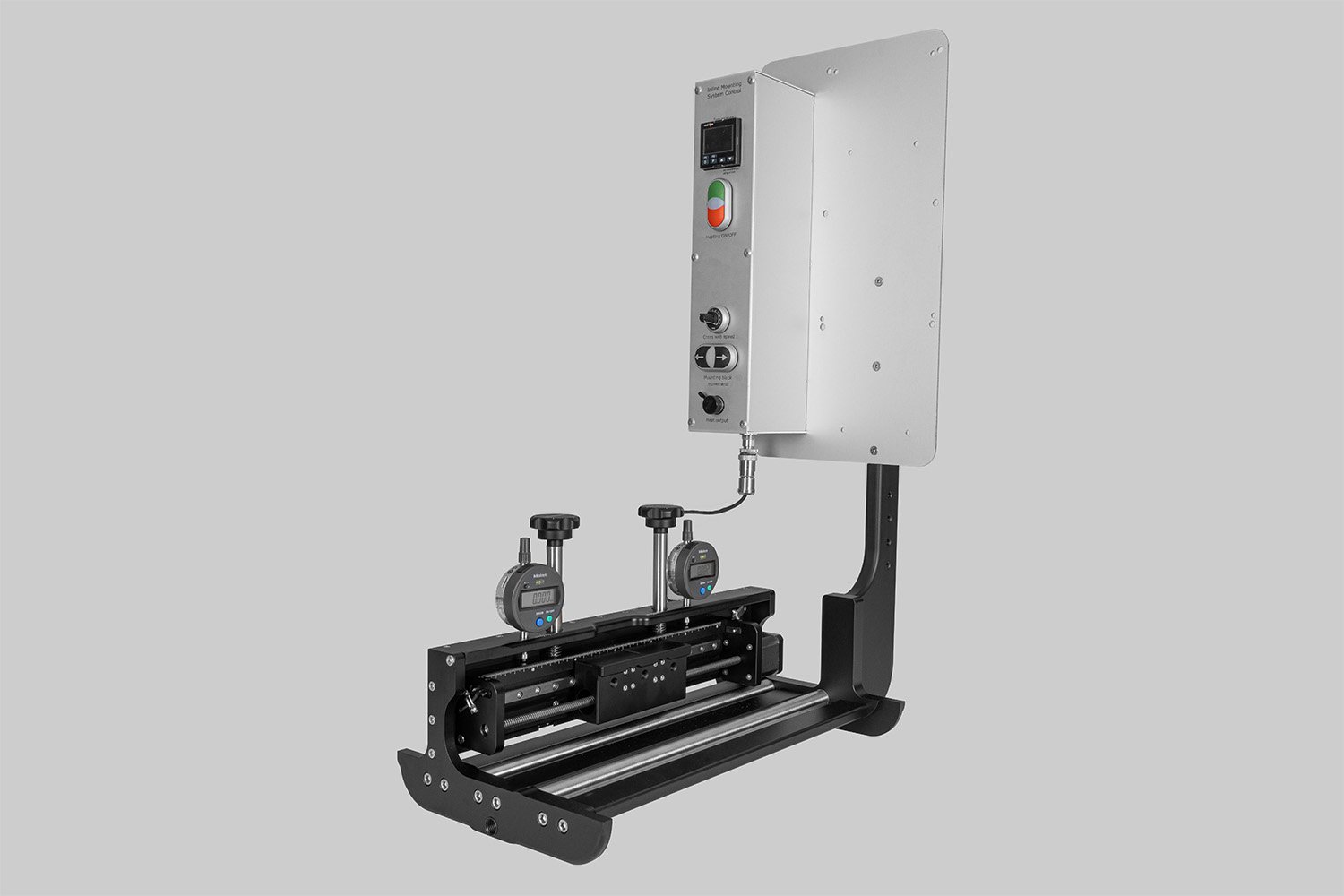
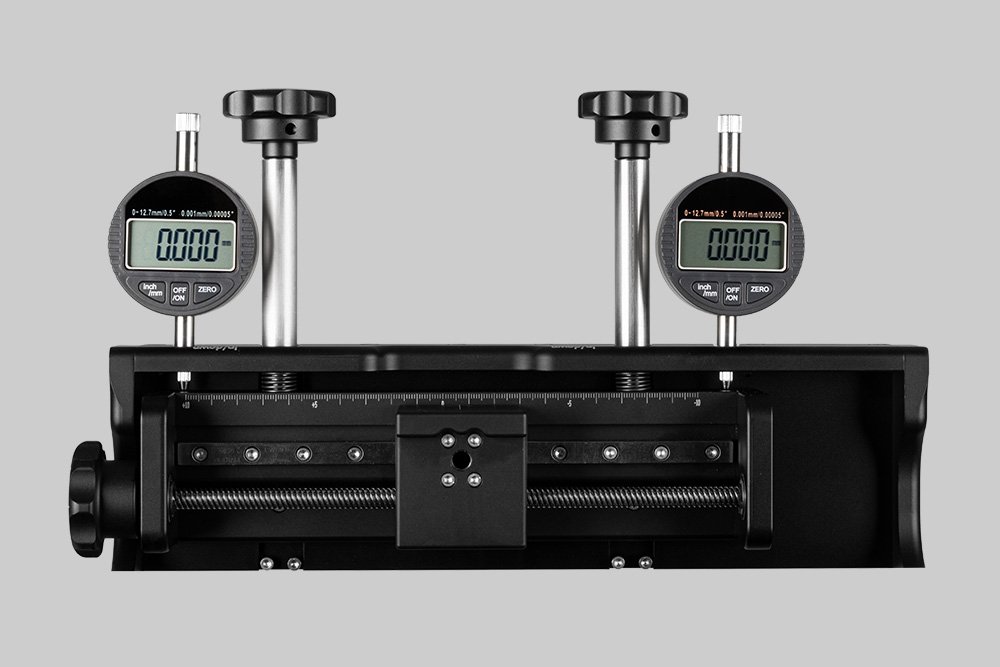
























Probably the World’s Most Compact R2R Slot-die Coater: A compact, fully integrated roll-to-roll coating platform for laboratories, complete with a mounting system, anodized rollers, a syringe pump, a 65 mm stainless slot-die head and an infrared oven system—delivering unmatched precision and scalability.